Electric cars are becoming a lot more prevalent on the roads. However, for those thinking of buying one, it’s often the charging issues which put them off. While more charging stations are being installed throughout the UK, drivers are often stuck figuring out how to charge the car at home.
Generally speaking, electric cars need to be charged with DC. However, the National Grid supplies power in AC. So, how can these vehicles be charged if you do decide to invest in them? Here, we’ll look at the differences between AC and DC charging for electric cars.
Understanding AC and A
AC and DC charging ultimately do the same thing – they charge an electric vehicle. However, the way in which they do this is slightly different.
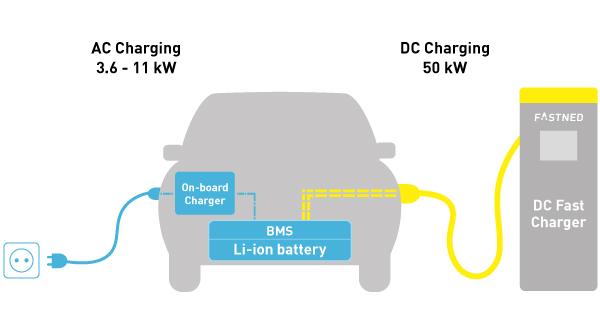
AC stands for alternating current and it can be used to charge a variety of electric vehicles. It’s supplied right from the power grid, giving you easy access to charging points when needed. Although electric cars use DC power, the AC is automatically converted to DC by the vehicle as it’s charging.
DC stands for Direct current and it tends to use a lot more power from the National Grid than AC. Vehicles charged with DC are charged from the outside, while vehicles using AC are charged from the inside. The power from both AC and DC is stored within the battery.
Which charges faster?
The type of current you use to charge an electric vehicle will impact how quickly it charges. For example, DC chargers are known to charge much faster than AC ones. This makes them ideal for those who need to charge up while they’re out on the road. This is because DC chargers can provide a current of up to 150kW. AC chargers on the other hand can only deliver up to 22kW.
DC charging occurs pretty quickly for the first 80%. However, for the final 20% charge, it does start to slow down a little. Still, an electric vehicle can be potentially fully charged with a DC charger in as little as 30 minutes.
AC requires an onboard charger, which is what slows down the charging rate. However, it does benefit from a consistent charging rate, meaning it won’t slow down as the car’s battery fills up. You can also improve charging capabilities through components sold by top company, RS Components.
As you can see, there are differences between AC and DC charging. DC tends to be much faster, although at the moment the majority of charging stations use AC.